© Turkuvaz Haberleşme ve Yayıncılık 2026
Initially released on Oct. 6, 2010, popular social media app Instagram turns 15 this week.
And while it has become one of the world’s most popular social networks with 3 billion monthly active users, it remains at the center of controversy due to certain restrictions on political content, data privacy concerns and its impact on young people's mental health.
Originally a social media platform for sharing photos and videos, Instagram has evolved into an app that many people habitually open every time they pick up their phone.
Instagram was developed by Kevin Systrom and Mike Krieger solely for photo sharing and launched on Oct. 6, 2010, in Apple’s App Store.
Downloaded by 25,000 people on its first day, the app quickly gained traction, reaching 1 million users within three months.
In its initial version, Instagram offered basic features, including uploading photos, liking, commenting, and following other users.
With the introduction of new camera effects in 2011 and the continual improvement of phone cameras, the rise of mobile photography helped accelerate Instagram’s growth.
By 2012, the platform surpassed 100 million users, and that same year, it was acquired by Facebook (now Meta) for around $1 billion.
In June 2013, Instagram evolved beyond being just a photo-sharing platform by adding video-sharing and messaging features.
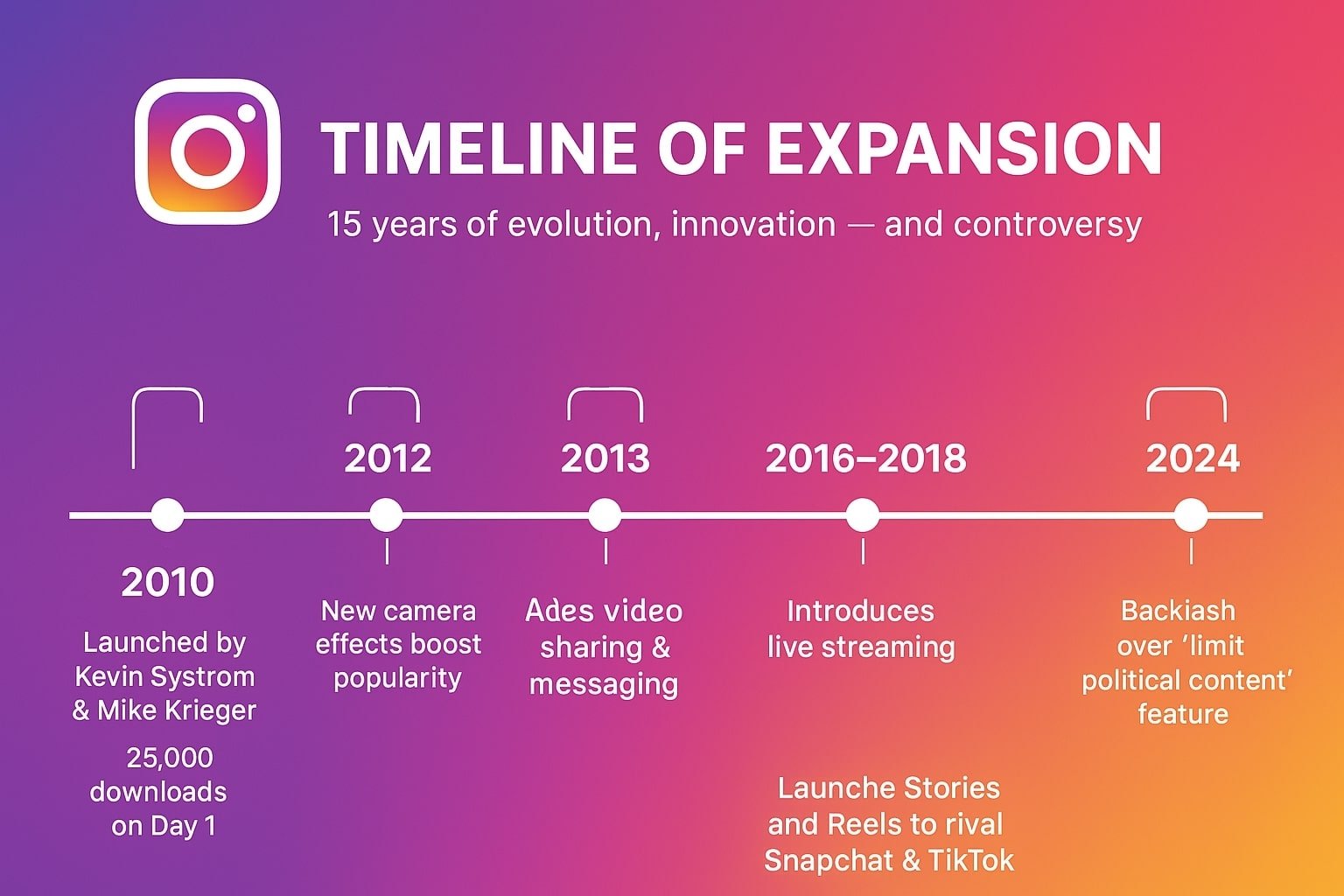
Three years later, the livestreaming feature was introduced, enabling users to share real-time moments with their followers.
In recent years, as competitors like Snapchat and TikTok have rapidly emerged, Instagram has developed similar features, such as Stories and Reels, to retain its user base.
Headquartered in California, Instagram has become one of the most influential global social media platforms with 3 billion monthly active users.
It has transformed into a central hub where trends in fashion, music, art and gastronomy are shaped. Beyond individual users, Instagram has also become a key player in digital marketing.
With every new feature, the platform has opened up new ways for businesses to reach wider audiences and enhance their marketing strategies.
Instagram’s popularity attracted numerous advertisers and played a significant role in ushering in the "influencer" era.
People with large social media followings, called influencers, began using their influence to promote specific products or services.
Starting in 2015, Instagram introduced more comprehensive advertising tools and from 2020, it strengthened its e-commerce capabilities with in-app shopping features.
At the same time, Instagram has also become a storefront for small businesses, helping brands, entrepreneurs and companies reach larger audiences through low-cost advertising options and shopping features.
Content creators have also been able to earn significant income through sponsored partnerships and subscription models, making Instagram a vital platform that supports entrepreneurship in the digital economy.
With a strong position in the global advertising market, Instagram has also contributed significantly to Meta’s ad revenues.
According to Business of Apps, an app industry analytics platform, Instagram generated an estimated $66.9 billion in revenue last year, accounting for approximately 40% of Meta’s total revenue.
Over its 15-year history, Instagram has been in the spotlight due to issues such as data privacy concerns, its impact on youth mental health and content restrictions.
The platform has faced legal actions worldwide. In 2022, the European Union fined Instagram 405 million euros for allegedly failing to protect children's personal data adequately.
In the U.S., 41 states filed a lawsuit in 2023, accusing Instagram and Facebook of harming children with addictive features.
Also in 2023, a $5 billion lawsuit was filed in the U.S. on behalf of a 13-year-old girl, alleging that Meta had intentionally made teens addicted to Instagram and exposed them to harmful content.
In 2024, Instagram triggered backlash after quietly enabling a “limit political content” feature without notifying users.
This setting, which was activated without users’ consent, led to allegations, especially during the U.S. elections and around pro-Palestine posts, that the visibility of political content was being deliberately reduced.
